Joint Pain
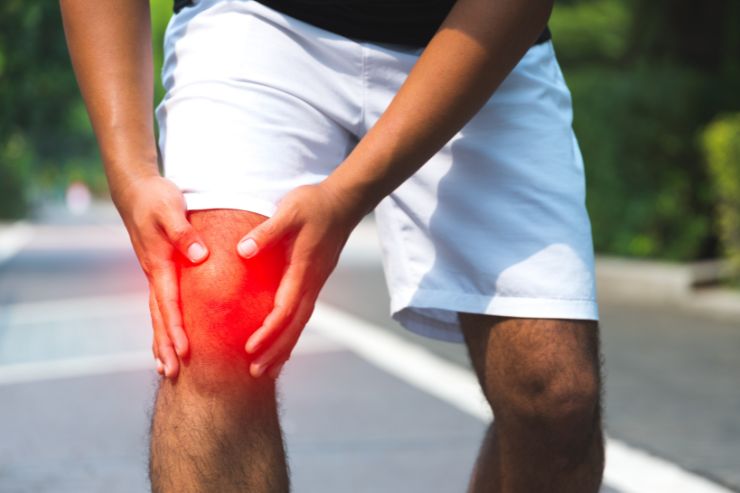
Joint pain refers to discomfort, aches, or soreness in any part of a joint, which may arise from a variety of causes. It can affect one or multiple joints, causing varying degrees of discomfort and impacting daily activities.
Causes of Joint Pain:
Arthritis: Conditions like osteoarthritis (wear and tear of joint cartilage), rheumatoid arthritis (autoimmune disorder), gout (crystals in joints), and lupus (autoimmune disease) commonly lead to joint pain.
Injury: Sprains, strains, fractures, or other injuries to joints can cause acute or chronic pain.
Overuse: Repetitive movements or excessive stress on joints from activities or occupations can lead to joint pain
Infection: Viral or bacterial infections affecting joints, such as septic arthritis.
Inflammation: Conditions like bursitis (inflammation of fluid-filled sacs) or tendinitis (inflammation of tendons) can cause pain around joints.
Age-related Changes: Wear and tear on joints over time, leading to conditions like degenerative joint disease.
Symptoms:
Pain: Persistent or intermittent discomfort in the joint, ranging from mild to severe.
Swelling: Inflammation around the joint, often accompanied by warmth and tenderness.
Stiffness: Reduced range of motion and difficulty moving the joint, especially after periods of inactivity.
Diagnosis and Treatment:
Diagnosis involves a medical history review, physical examination, and sometimes imaging tests like X-rays or MRI. Treatment varies based on the underlying cause but may include:
Medications: Pain relievers, anti-inflammatories, or disease-modifying drugs for arthritis.
Physical Therapy: Exercises to strengthen muscles around the joint, improve flexibility, and reduce pain.
Rest and Ice: Resting the joint and applying ice packs to reduce inflammation and pain.
Lifestyle Changes: Weight management, ergonomic adjustments, and modifying activities to reduce joint stress.
Surgery: In severe cases or when conservative treatments fail, surgical options like joint replacement or arthroscopy may be considered.
Management and Outlook:
Effective management of joint pain often requires a multidisciplinary approach involving healthcare providers, physical therapists, and sometimes specialists. Early intervention and comprehensive care can help manage symptoms, improve joint function, and enhance overall quality of life.

